What Is The Weakest Base
| STRONG AND WEAK BASES This folio explains the terms potent and weak every bit applied to bases. As a part of this it defines and explains Thousandb and pKb. Nosotros are going to use the Bronsted-Lowry definition of a base as a substance which accepts hydrogen ions (protons). | ||||||||||||||||
| Annotation:If you don't know what the Bronsted-Lowry theory is, you should read virtually theories of acids and bases on another page in this department. Yous don't need to spend time reading nigh Lewis acids and bases for the purposes of this present folio. Use the Back button on your browser when you are ready to return to this page. | ||||||||||||||||
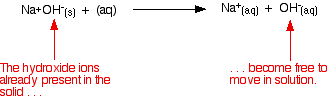
| The usual way of comparison the strengths of bases is to see how readily they produce hydroxide ions in solution. This may be because they already comprise hydroxide ions, or because they take hydrogen ions from water molecules to produce hydroxide ions. Strong bases Explaining the term "strong base" A strong base of operations is something like sodium hydroxide or potassium hydroxide which is fully ionic. You tin recall of the compound as being 100% split up into metal ions and hydroxide ions in solution. Each mole of sodium hydroxide dissolves to give a mole of hydroxide ions in solution. Some stiff bases like calcium hydroxide aren't very soluble in water. That doesn't affair - what does dissolve is still 100% ionised into calcium ions and hydroxide ions. Calcium hydroxide still counts as a strong base because of that 100% ionisation. Working out the pH of a strong base of operations Remember that: Since pH is a measure of hydrogen ion concentration, how can a solution which contains hydroxide ions accept a pH? To understand this, you demand to know most the ionic product for water. | ||||||||||||||||
| Of import:If you don't understand about the ionic product for h2o you must follow this link before yous go on. Use the BACK button on your browser when you are ready to return to this folio. | ||||||||||||||||
| Wherever at that place is water, an equilibrium is set up. Using the simplified version of this equilibrium: In the presence of extra hydroxide ions from, say, sodium hydroxide, the equilibrium is however there, simply the position of equilibrium has been shifted well to the left according to Le Chatelier'southward Principle. | ||||||||||||||||
| Annotation:If you don't understand Le Chatelier's Principle, you lot should follow this link earlier you get on. Make sure that you understand the effect of concentration on position of equilibrium. Use the Back button on your browser when y'all are ready to render to this page. | ||||||||||||||||
| At that place volition be far fewer hydrogen ions than there are in pure water, but at that place will still be hydrogen ions present. The pH is a measure of the concentration of these. An outline of the method of working out the pH of a strong base
An case To notice the pH of 0.500 mol dm-3 sodium hydroxide solution: Because the sodium hydroxide is fully ionic, each mole of it gives that same number of moles of hydroxide ions in solution. | ||||||||||||||||
| Notation:You lot would have to be careful here if you had a base of operations similar calcium hydroxide, Ca(OH)2. Each mole of calcium hydroxide would produce twice as many hydroxide ions in solution. | ||||||||||||||||
| Now you employ the value of Kw at the temperature of your solution. You normally have this as ane.00 ten 10-14 mol2 dm-6. This is true whether the water is pure or not. In this case we accept a value for the hydroxide ion concentration. Substituting that gives: If you solve that for [H+], and so catechumen it into pH, y'all go a pH of thirteen.7. | ||||||||||||||||
| Note:If y'all want more than examples to expect at and to try yourself (with fully worked solutions given), you may exist interested in my chemistry calculations book. This also includes the contrary problem which is slightly more confusing - working out the concentration of a potent base from its pH. | ||||||||||||||||
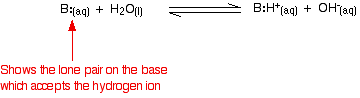
| Weak bases Explaining the term "weak base of operations" Ammonia is a typical weak base. Ammonia itself plainly doesn't incorporate hydroxide ions, but it reacts with h2o to produce ammonium ions and hydroxide ions. Still, the reaction is reversible, and at any one fourth dimension about 99% of the ammonia is still present as ammonia molecules. Just about 1% has actually produced hydroxide ions. A weak base is one which doesn't convert fully into hydroxide ions in solution. | ||||||||||||||||
| Important:What follows isn't required past any of the current United kingdom of great britain and northern ireland A' level syllabuses. | ||||||||||||||||
| Comparing the strengths of weak bases in solution: Gb When a weak base reacts with water, the position of equilibrium varies from base to base. The further to the left information technology is, the weaker the base. You can go a measure of the position of an equilibrium by writing an equilibrium abiding for the reaction. The lower the value for the constant, the more the equilibrium lies to the left. In this instance the equilibrium constant is called Yardb. This is defined as: | ||||||||||||||||
| Note:If you want to know why the water has been omitted from the bottom of this expression, you will find it explained on the page near potent and weak acids under the corresponding abiding, Ka. Use the Back button on your browser when you are gear up to render to this folio. | ||||||||||||||||
| pKb The relationship between Kb and pKb is exactly the aforementioned as all the other "p" terms in this topic: The table shows some values for Kb and pKb for some weak bases.
Every bit y'all go down the table, the value of Kb is increasing. That ways that the bases are getting stronger. As Kb gets bigger, pKb gets smaller. The lower the value of pKb, the stronger the base. This is exactly in line with the corresponding term for acids, pKa - the smaller the value, the stronger the acid. | ||||||||||||||||
| Annotation:If you are interested in exploring organic bases further, you volition find them explained elsewhere on the site. | ||||||||||||||||
| Questions to test your agreement If this is the first set of questions you have washed, please read the introductory folio earlier you start. You will need to use the BACK Push button on your browser to come back hither afterward. questions on strong and weak bases answers
To the acid-base equilibria card . . . To the Physical Chemistry carte . . . To Main Bill of fare . . . © Jim Clark 2002 (modified November 2013) | ||||||||||||||||
What Is The Weakest Base,
Source: https://www.chemguide.co.uk/physical/acidbaseeqia/bases.html
Posted by: leewhapin.blogspot.com

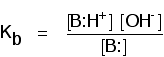

0 Response to "What Is The Weakest Base"
Post a Comment